The realm of vocational education is continuously evolving, reflecting the ever-changing dynamics of the job market. As we step into 2025, what was once known as vocational education has undergone a transformation in both name and approach. Today, it's frequently called Career and Technical Education, or CTE. This shift isn't just a matter of semantics; it signifies a broader, more inclusive view of equipping individuals with practical skills that seamlessly integrate with industry demands.
With advances in technology, vocational education now incorporates cutting-edge tools and digital training, helping individuals stay relevant in an increasingly tech-centric world. The focus has grown from traditional trades to encompass a variety of fields, including IT, healthcare, and green technologies. These programs aim to provide a direct pipeline from education to employment, ensuring that learners gain hands-on experience and industry certifications that make them job-ready.
- Evolving Terminology
- Modern Vocational Programs
- Importance of Skill-Oriented Learning
- Integration of Technology in Vocational Education
- Career Opportunities and Future Trends
Evolving Terminology
The shift from vocational education to what we now commonly refer to as Career and Technical Education (CTE) reflects more than just a change in nomenclature. This evolution highlights a transformative approach in how skills for the workforce are taught and valued, responding to the diversified needs of our modern economy. Vocational education was traditionally associated with manual or industrial occupations, often viewed as less prestigious than academic education. However, the landscape has dramatically changed, recognizing that specialized skills are critical in every sector from technology to healthcare.
One of the driving forces behind this shift is the growing demand for skills that match the fast-paced changes in global industries. The emphasis has moved towards an educational paradigm where acquiring skills is as crucial as academic knowledge. In the United States, for example, CTE is supported by substantial federal funding under the Carl D. Perkins Career and Technical Education Act, which underscores its significance in preparing the workforce. According to UNESCO, technical and vocational education and training (TVET) is pivotal in reducing unemployment and fostering innovation. This global recognition of vocationally-centered education demonstrates how language and focus have evolved alongside policy and economic trends.
Integration and Impact
The current terminology reflects integrating technical training into curricula from high school onward, making education more inclusive and tailored to individual career goals. Enhanced by partnerships between educational institutions and industries, students can now gain real-world experience and apply what they learn in classrooms directly to their chosen fields. For instance, digital literacy has become a non-negotiable component, preparing students for careers in industries such as information technology and digital marketing. Programs not only spotlight traditional craftsmanship but also introduce learners to emerging sectors like renewable energy, artificial intelligence, and biotechnology."In our rapidly advancing world, CTE bridges the gap between secondary education and high-paying, high-demand careers," stated Dr. James Stone, an education expert with over three decades of experience. His insight suggests that a robust CTE system can reduce skill shortages and prosperity disparities across nations.
CTE isn't merely about terminology. It has become synonymous with modernity in education, representing a holistic approach where academic knowledge and practical skills coalesce to create versatile, employable professionals. This trend is mirrored globally as more countries adopt frameworks supporting technical education and training, recognizing its substantial role in economic development.
Modern Vocational Programs
In today's rapidly evolving job market, the significance of vocational education programs cannot be overstated. These programs, once narrowly focused on trades like carpentry or plumbing, have now expanded to embrace a multitude of disciplines, reflecting the diverse needs of contemporary industries. One of the cornerstones of modern vocational education is the concept of skill development, emphasizing the acquisition of abilities that are directly applicable in real-world settings. This approach ensures that students are not only knowledgeable but also proficient in practical tasks they will encounter in their professional lives. This hands-on experience is invaluable, allowing learners to bridge the gap between theory and practice efficiently.
A noteworthy aspect of these programs is their adaptability to technological advancements. With sectors such as information technology and healthcare experiencing exponential growth, vocational courses have evolved to incorporate these vital areas. For instance, many institutions now offer specialized courses in cybersecurity, data analysis, and health informatics, all of which are crucial in today's digital age. These courses are designed with input from industry experts, ensuring that the curriculum remains relevant and up-to-date, thus making graduates highly employable.
According to a report by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), "the integration of technology with vocational training is one of the most significant trends in education, providing graduates a distinct edge in the competitive job market."
Moreover, many vocational programs now offer certifications that are recognized globally, enabling students to pursue opportunities without geographical limitations. This international recognition is essential for those who aspire to work in foreign markets or multinational corporations. The flexibility of these programs is another key advantage; many offer part-time or online courses, catering to working professionals who wish to enhance their skills while maintaining their current job.
Career training through vocational courses has also become more interdisciplinary. Students can now tailor their education by selecting modules that align with their career goals or interests. For example, someone interested in sustainable development can opt for courses in environmental science alongside traditional studies. This tailored approach empowers students, offering them greater control over their educational journey and better preparing them for the demands of the global workforce.
The shift towards a more comprehensive technical courses system marks the beginning of a new era in education. With these programs continually adapting to meet the emerging needs of various sectors, they play a critical role in shaping the workforce of tomorrow. As industries continue to evolve, staying informed about the latest trends in vocational education can open up a world of possibilities for those looking to advance their careers.
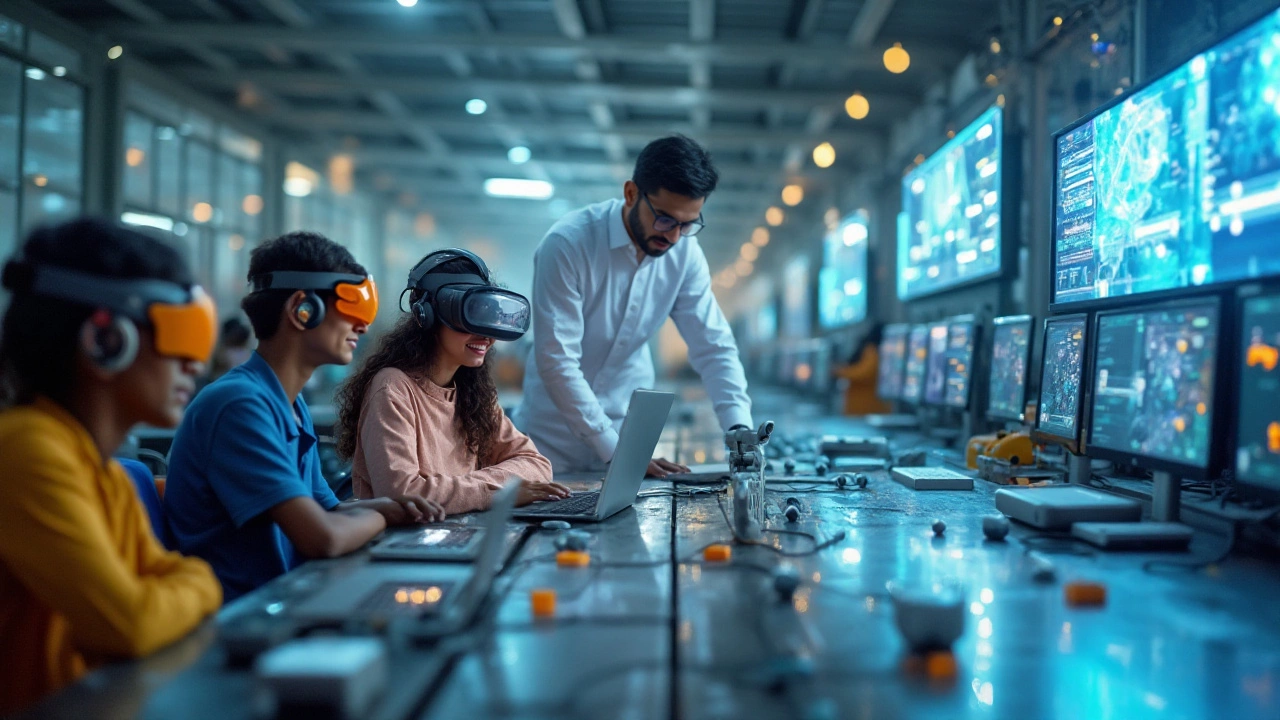

Importance of Skill-Oriented Learning
The significance of skill-oriented learning has never been more pronounced than in today's fast-paced world. Vocational education is evolving to prioritize practical, applicable skills that align with real-world demands. In many ways, this shift addresses the growing skills gap observed worldwide, where traditional education models fall short of preparing students for the exact needs of today's employers. Lessons are no longer confined to textbooks, as the emphasis is placed on experiential learning—an approach that garners enthusiasm and engagement among students eager to enter diverse industries.
Many experts agree that by prioritizing skills over theoretical knowledge, students gain a tangible understanding of their field, leading to better job satisfaction and performance. Notably, a Forbes report highlighted that 65% of today's students will work in jobs that do not yet exist, underscoring the importance of a flexible, skills-based education that can adapt to unprecedented changes in industry. This adaptability is crucial in industries such as technology and healthcare, where constant advancements and innovations require a workforce adept in learning and applying new techniques quickly.
"Education is not the learning of facts, but the training of the mind to think," as famously stated by Albert Einstein, captures the essence of what skill-oriented learning strives to achieve.
Technical courses within vocational education equip students with practical skills, such as coding, welding, or culinary arts, which can be directly applied to various careers. Education policymakers and industry leaders stress that fostering these abilities at an early stage not only enhances individual career prospects but also bolsters the economic fabric by creating a versatile workforce. The typical modules now incorporate both theoretical understanding and significant hours of hands-on training, allowing learners to acquire industry certifications that employers recognize and trust.
There's also a personal development angle to skill-oriented learning. Beyond career prospects, such an approach inculcates problem-solving skills, teamwork, and resilience among students. These are vital life skills that contribute positively beyond the workplace. It's worth noting that vocational learners, who hone their skills from a young age, often exhibit heightened creativity and initiative, both valuable assets in an individual's personal and professional life. With the growing importance of skill development, vocational training is centered not just on creating workers, but innovators and leaders who are equipped for future challenges, ensuring that both skill sets and mindsets are aligned for success.
Integration of Technology in Vocational Education
In today's fast-paced world, the integration of technology in vocational education is a game-changer, transforming how students acquire **technical courses** and vital skills necessary for dynamic workplaces. This transformation hasn't happened overnight but is the result of concerted efforts to harness technology's potential to enhance learning experiences. Interactive simulations, online learning platforms, and digital assessment tools exemplify the myriad ways technology empowers students in vocational settings. Platforms like Khan Academy and Coursera have become pivotal, allowing learners worldwide to access high-quality education at their convenience, thus breaking down regional and financial barriers.
This technological shift is not just about supplementing traditional teaching methods; it is about fundamentally changing how vocational education is delivered. By simulating real-world environments and challenges, virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) offer immersive experiences that mirror actual workplace scenarios. Imagine a welding student perfecting their techniques in a virtual workshop or a healthcare trainee practicing emergency response in a simulated crisis. These tools enrich conceptual understanding and provide a safe space for honing practical skills.
As industries increasingly rely on technology, vocational education must stay ahead of the curve by incorporating new and emerging tech trends. For example, coding, data analysis, and machinery automation are now integral to many vocational programs, reflecting the growing relevance of IT across sectors. This adaptation helps students remain competitive, as they step into roles that once required highly specialized tech skills. According to a survey by the World Economic Forum, approximately 50% of all employees will need reskilling by 2025, highlighting the significance of technology-driven training in vocational curriculums.
Moreover, mobile technology has contributed significantly to making **career training** more accessible. Through mobile apps, students can access instructional content, engage with instructors, and even participate in peer forums. This flexibility accommodates diverse lifestyles, encouraging lifelong learning among working professionals and independent learners. The responsive design of these platforms ensures that learners can switch seamlessly between devices, maintaining continuity and momentum in their training journeys. As mentioned in a recent MIT study, technology in education doesn't just support learning—it can transform it.
"Education technology can play a significant role in transforming how skills are acquired and applied," stated Professor John Watson from the Technology and Education Commission.
For educators, integrating technology into vocational courses involves rethinking pedagogical approaches to ensure that students not only gain technical proficiency but also develop digital literacy. Professional development programs are increasingly focused on equipping instructors with the latest tech tools and instructional strategies needed to foster an engaging and effective learning environment. This shift towards tech-enhanced education is crucial in preparing students for modern workplaces where technological competency is indispensable.

Career Opportunities and Future Trends
As we navigate through the mid-2020s, the landscape of career training and vocational education continues to reinvent itself, unlocking myriad possibilities for learners and redefining job markets. The rapid integration of technology into almost every industry has resulted in a demand for new skill sets, prompting vocational programs to swiftly adapt. Courses that once focused on a singular technical expertise now offer a blend of skills, combining traditional methods with digital learning and interdisciplinary approaches. This is reshaping how students prepare for the workforce, making them adaptable in a fast-changing environment.
A significant aspect powering this change is the shift in industries thriving at the forefront of economic growth. Emerging sectors such as renewable energy, cybersecurity, and digital marketing are seeking candidates with practical training and industry-specific knowledge, emphasizing the impact of skill-driven education. These sectors not only promise stable careers but also actively contribute to sustainable development and innovation. For instance, a trained professional in green technologies might find roles ranging from project manager in a solar energy company to a consultant for sustainable building practices.
The job market is also witnessing a rise in freelance and gig economy opportunities, compelling vocational courses to integrate entrepreneurial skills into their curricula. This prepares students for flexible work environments where they can leverage their technical abilities as independent contractors or business owners. Industry partnerships are becoming more common in vocational education, facilitating real-world experience through internships and apprenticeships, which enhance employability and provide networks for job placements. According to the World Economic Forum, almost 50% of all employees will need reskilling by 2025, indicating a pressing need for evolving educational structures.
"Education plays a crucial role in enhancing workforce readiness, and vocational training is at the heart of this transformation," shared John Rowe, a renowned educational consultant.
Looking ahead, the horizon appears promising with vocational education embracing AI and machine learning, creating versatile programs that adjust to individual learning paces and provide personalized pathways. This change not only boosts student engagement but also optimizes learning outcomes. The rise of hybrid educational models that combine online and offline elements is expected to continue, offering accessible learning options for diverse communities. As new employment patterns develop, vocational schools are also emphasizing lifelong learning by offering post-graduate certifications and advanced diplomas, allowing professionals to stay ahead in their fields.
The shift towards a skill-based economy, underscored by an increased recognition of technical courses, underscores the importance of flexible and responsive education systems. Collaborative efforts between governments, educational institutes, and industries remain critical in shaping these programs, ensuring that they reflect current trends while anticipating future demands. As vocational education continues to meet and exceed these goals, it paves the way for a workforce that is not only skilled but also resilient, ready to tackle the challenges of a dynamic global economy.